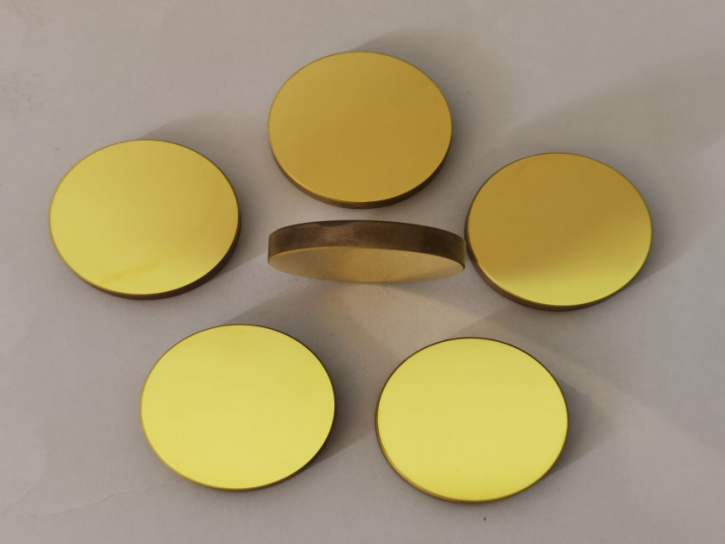
Product display
Silver-plated reflective glass





Classification:
Key words:
Silver-plated reflective glass
E-mail:
- Product Introduction
- Product Parameters
- Transmittance
- Product Picture
- Processing technology
- Optical use
- Custom Specifications
- Technical Answers
-
- Commodity name: Silver-plated reflective glass
Metallic reflective films are usually composed of a single metal layer, which has the advantages of high reflectivity and wide spectral range.
Metallic reflective films are usually composed of a single metal layer, which has the advantages of high reflectivity and wide spectral range. The principle of this reflective film is based on the reflection of light. When the light is irradiated on the metal surface, the incident light is reflected back to the original medium by the metal layer, thereby realizing the reflection of the light. The advantage is that the preparation process is simple and the working wavelength range is wide.
However, its light loss is large, and the reflectivity cannot be high. In order to further improve the reflectivity, several dielectric layers with a certain thickness can be plated on the outer side of the film to form a metal dielectric reflective film. In general, metal reflective film is a kind of optical film with important application value, and has a wide range of applications in the field of optics.
-
fused silica Protection gold 0°-45° Customizable >90% Silicon Protection gold 0°-45° Customizable >90% K9 Glass Protection gold 0°-45° Customizable >90% fused silica PROTECTION SILVER 0°-45° Customizable >90% Silicon PROTECTION SILVER 0°-45° Customizable >90% K9 Glass PROTECTION SILVER 0°-45° Customizable >90% fused silica Aluminum protection 0°-45° Customizable >90% Silicon Aluminum protection 0°-45° Customizable >90% K9 Glass Aluminum protection 0°-45° Customizable >90% -
The information is being sorted out......
-
 Silver-plated reflective glass
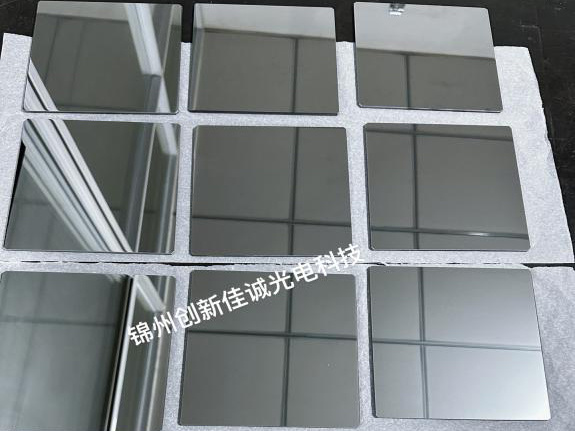
Silver-plated reflective glass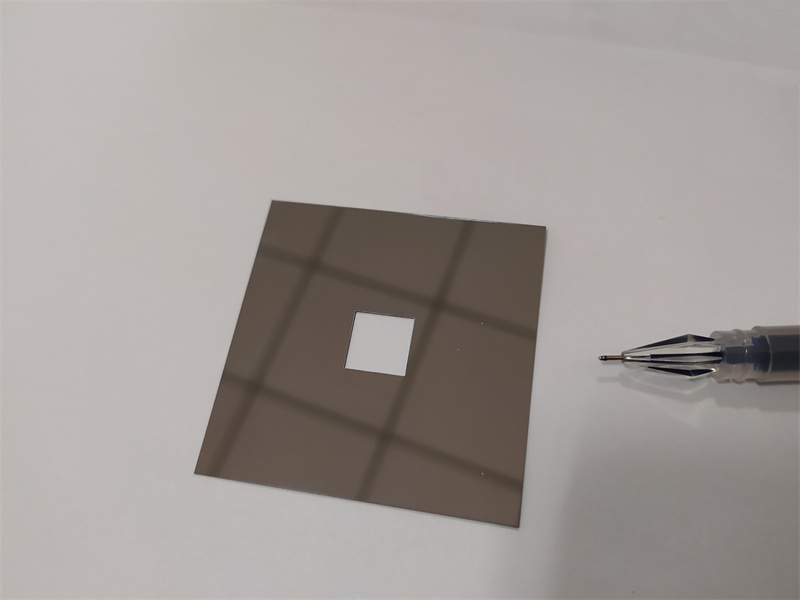 Silver-plated glass
Silver-plated glass Perforated silver-plated glass
Perforated silver-plated glass silvered mirror
silvered mirror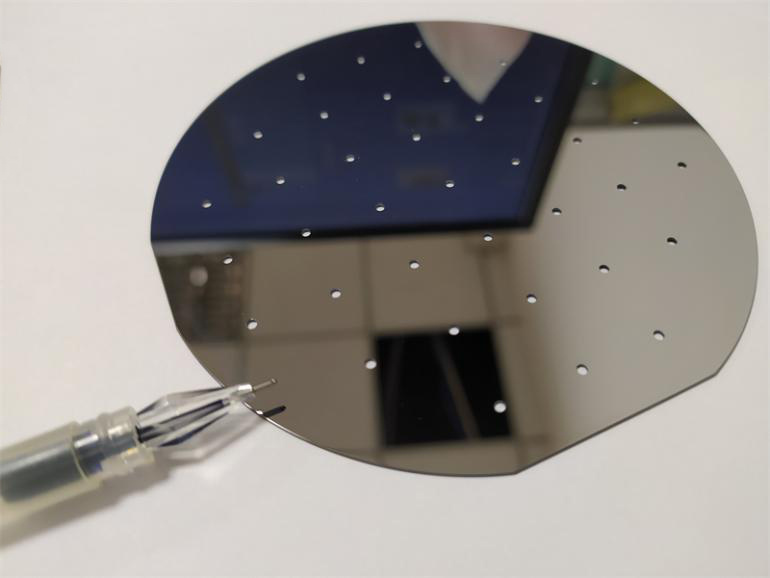 quartz glass black film
quartz glass black film -
coating process
Optical coating concept and principle
Coating is to use physical or chemical methods to plate a layer of transparent electrolyte film on the surface of the material, or plate a layer of metal film, the purpose is to change the reflection and transmission characteristics of the surface of the material, to reduce or increase the reflection of light, beam separation, color separation, filtering, polarization and other requirements. Commonly used coating methods include vacuum coating (a kind of physical coating) and chemical coating. After the surface of the optical parts is coated, the light is reflected and transmitted multiple times on the film layer to form multi-beam interference, and the refractive index and thickness of the film layer can be controlled to obtain different intensity distributions. This is the basic principle of interference coating.
optical film classification:
The coating: silicon, germanium, zinc sulfide, zinc selenide and other substrates are more, fluoride is rare.
Single wavelength, dual wavelength, broadband
Reflective film: sub-dielectric and metal reflective film, metal reflective film is generally gold-plated plus protective layer.
Semi-reflective, single-wavelength, dual-wavelength, broadband
Hard carbon film: also called DLC film, generally plated on the outer surface of silicon, germanium, chalcogenide glass for protection/antireflection. The other side of the product generally requires antireflection coating.
Split film: some require specific incident angle, visible light band reflection, infrared band through, more used in spectral analysis.
45 degree beam splitter, two-color beam splitter, polarization beam splitter & prism
Filter film: broadband, narrowband
Laser Crystal Film: YAG/YV04/KTP/LBO/BBO/LIND03
UV film-antireflection: 193/248/266/308/340/355, aluminum reflection 180-400nm
Infrared film: CO210.6UM/YAG2940NM/SI & GE & ZNSE & ZNSCoating process and equipment
Cleaning equipment:
Ultrasonic cleaning machine: refers to the integration of cleaning and drying, can be directly loaded plate coating. At the same time, the machine must be used in clean space;
Ultrasonic cleaning technology for optical lenses:
In optical cold processing, the cleaning of the lens mainly refers to the cleaning of the residual polishing liquid, adhesive and protective material after the lens is polished. Cleaning of grinding oil and glass powder after lens edge grinding; Cleaning of finger marks, saliva and various attachments before lens coating.
The traditional cleaning method is the use of wiping materials (gauze, dust-free paper) with chemical reagents (gasoline, ethanol, acetone, ether) to soak, wipe and other means of manual cleaning.
This method is time-consuming and laborious, has poor cleanliness, and is obviously not suitable for the modern large-scale optical cold processing industry. This forced people to look for a mechanized means of cleaning instead. So ultrasonic cleaning technology gradually into the optical cold processing industry and show their skills, and further promote the development of optical cold processing industry.
The basic principle of ultrasonic cleaning technology can be roughly considered to be a method that uses the huge force generated by the ultrasonic field to promote a series of physical and chemical changes in the washing medium to achieve the purpose of cleaning.
When the high frequency vibration higher than the sound wave (28~40khz) is transmitted to the cleaning medium, the liquid medium produces nearly vacuum cavity bubbles under the high frequency vibration. In the process of collision, merger and extinction of the cavity bubbles, the liquid can instantly generate thousands of atmospheric pressure pressure, and such a large pressure makes a series of physical and chemical changes occur in the surrounding substances.
Process flow:

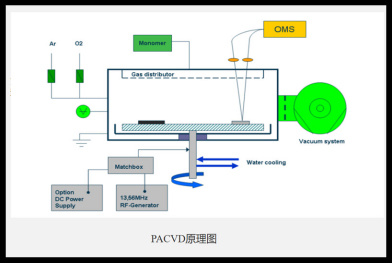
Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD):
It is to ionize the gas containing the atoms of the film by means of microwave or radio frequency to form plasma locally, and the plasma has strong chemical activity and is easy to react to deposit the desired film on the substrate. PECVD can be achieved at lower temperatures because the activity of plasma is used to promote chemical reactions.
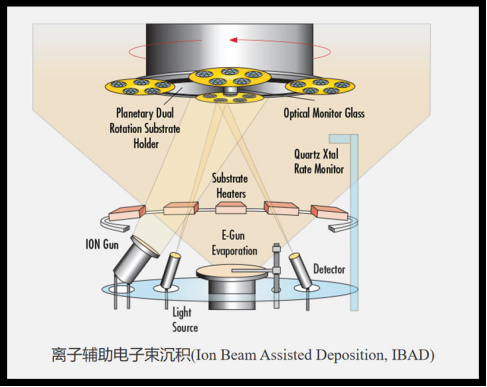
plasma assisted vapor deposition:
At present, the preparation method of DLC film is commonly used. Using radio frequency technology (RF-PACVD) will be introduced into the gas (butane, argon) ionization, in the plate from the bias (negative) attraction, positively charged particles to the substrate impact, deposited on the surface of the substrate.
-
Use Related industries optical instrument It plays an important role in optical instruments, such as telescopes, microscopes, sights, etc., which can improve resolution and imaging quality. Laser Technology It plays the role of reflection and focusing in the laser system, which can improve the transmission efficiency and accuracy. Photoelectric sensor
In the photoelectric sensor, it plays the role of anti-reflection and increase the transmittance, which can improve the performance and response speed of the sensor. Solar cell
It plays the role of reflection and transmission control in the solar cell, which can improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency and reduce the cost. Display
In the display, it plays a role of anti-reflection and improving transmittance, which can improve display effect and viewing experience. Electronic Equipment It plays the role of electromagnetic shielding and heat dissipation in electronic equipment, which can protect electronic equipment from electromagnetic interference and overheating. -
The information is being sorted out......
-
Function:Its function is to increase the reflectivity of the optical surface.
Category:Reflective films can generally be divided into two categories, one is a metal reflective film, and the other is an all-dielectric reflective film. In addition, there is a metal-dielectric reflective film combining the two.
metal reflective film:Generally, metals have a large extinction coefficient. When the light beam is incident on the metal surface by air, the light amplitude entering the metal is rapidly attenuated, so that the light energy entering the metal is correspondingly reduced, and the reflected light energy is increased. The larger the extinction coefficient, the more rapidly the light amplitude attenuates, the less light energy enters the metal, and the higher the reflectivity.
dielectric reflective film:The dielectric reflective film is based on multi-beam interference. Contrary to the antireflection film, the reflectivity of the optical surface can be increased by plating a thin film on the optical surface with a refractive index higher than that of the base material. The simplest multilayer reflection is formed by alternating evaporation of two materials with high and low refractive indices, and the optical thickness of each film is a quarter of a certain wavelength. Under this condition, the reflected light vectors on the surfaces participating in the superposition vibrate in the same direction. The synthetic amplitude increases with the increase of the number of layers of the film.
metal reflective film
In optical thin films, highly reflective films and antireflective films are almost as important. A highly reflective film is an optical element that reflects most or almost all of the incident light energy back. Some mirrors are required to have a sufficiently high reflectivity, and there is no requirement for the absorption and transmittance of the film, and they can be used with a simple metal film to meet the common requirements. In some applications, if the desired reflectivity is higher than the metal film can achieve, the metal film can be plated with an additional dielectric layer to improve their reflectivity. There are also some mirrors that require not only a large reflectivity, but also a minimum absorption rate. These mirrors use all-dielectric multilayer reflective films.
The materials commonly used for plating metal reflective films are aluminum (Al), silver (Ag), gold (Au), etc., and their spectral reflectance curves are shown in Figure 3-7. Aluminum film is the only material with high reflectivity from ultraviolet region to infrared region. At the same time, a thin aluminum oxide (AlOg) film can be generated on the surface of aluminum film in the atmosphere, which plays the role of protective film layer, so the film layer is relatively firm and stable. For the above reasons, the application of aluminum film is very wide. The silver film has high reflectivity in both the visible and infrared regions, and the polarization effect introduced is minimal when used obliquely. However, the use of the evaporated silver film as a coating for front surface mirrors is severely limited for two reasons: it has poor adhesion to the glass substrate; and it is susceptible to the influence of sulfides and tarnishes. Attempts to use evaporated silicon monoxide or magnesium fluoride as a protective film have been unsuccessful due to their poor adhesion to silver. Therefore, it is usually only used for short-term effects or as a coating for rear surface mirrors. The reflectivity of the gold film in the infrared region is very high, and its strength and stability are better than that of the silver film, so it is often used as an infrared mirror. The adhesion of the gold film to the glass substrate is poor, and the chromium film is often used as the substrate layer. If the deposition of the gold film is supplemented by ion beam bombardment, the adhesion of the gold film to the substrate can be significantly improved.
Common metal film reflectivity curve
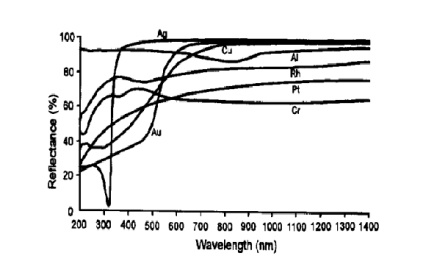
Since most metal films are relatively soft and easy to damage, they are often plated with a protective film outside the metal film. This can both improve the strength and protect the metal film from the atmosphere. After the protective film is plated, the reflectivity of the mirror will decrease more or less, and the higher the refractive index of the protective film, the more the reflectivity decreases. The most commonly used protective film is silicon monoxide, in addition, aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is also often used as an aluminum protective film. Al2O3 can be prepared by electron beam vacuum evaporation or anodization of aluminum films. The aluminum mirror protected by anodizing has very good mechanical strength.
Classification:
The reflective film is divided into dielectric high-reflection film and metal high-reflection film;
Among them, metal high anti-film is common.
Reinforced Aluminum: R>90% @ 400-700nm
Protective Aluminum: R>87% @ 400-1200nm
UV Protected Aluminum: R>80% @ 250-700nm
Protection Silver: R>95% @ 400-12000nm
Enhanced Silver: R>98.5%@ 700-1100nm
Protection gold: R>98% @ 2000-12000nm;Metal films are all aimed at broadband bands, and there is no incident angle limit, but the reflectivity is relatively low. Compared with metal films, dielectric films are generally aimed at single-point wavelengths and can also be aimed at broadband bands. However, under the condition of ensuring reflectivity, the bandwidth is generally narrow, usually around 300-400nm, and with incident angle limit, the reflectivity can usually reach more than 99% or even higher. For example, HR @ 532nm,R>99.8, AOI = 45; Or HR @ 400-700nm,R>99.5, AOI = 45, of course, other single angles or wide incident angles (such as 0-45) can also be made, but the reflectivity will also change accordingly.
several kinds of common metal coating:
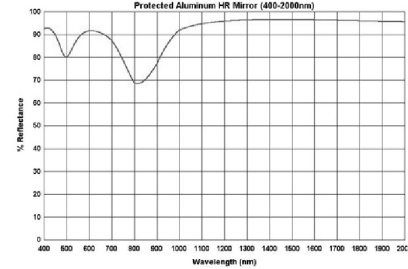
1) Protect aluminum: The thin metal material commonly used in the ultraviolet region is aluminum, and aluminum (and silver) is commonly used in the visible region
R>88% @ visible region
2) protection of silver, infrared area commonly used gold, silver
> 95% visible region
> 98% micron infrared region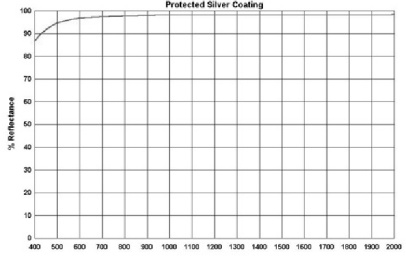
3) Protective gold: very high reflectivity in the infrared region after 0.65 microns
> 95% 0.65-2 microns
> 98% 2-12 micron infrared light area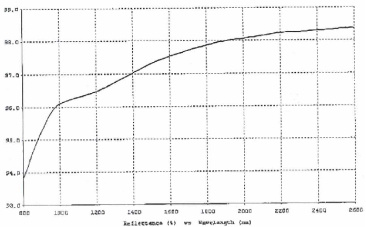
high reflective filmMetal Mirror (Metallic Mirror)
The cost is low and the reflection band is wide.
It is generally used for applications where the reflectivity requirement is not particularly high, but the band is very wide.
The presence of partial absorption limits its application in the laser field.All-dielectric mirror (Dielectric HR coatings)
The cost is higher and the reflection band is narrow.
The reflectivity can be very high.
The reflection band range is limited. If the reflection band range is increased, the difficulty of film plating will increase.
The film layer is thicker, the stress is larger, and there is a risk of film layer falling off.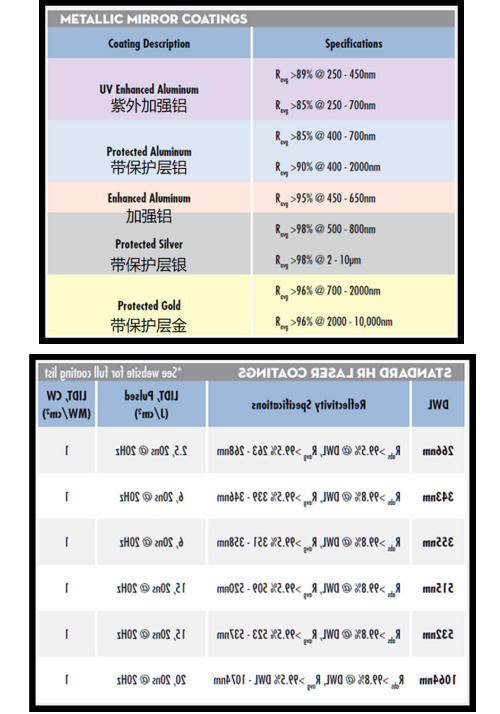
Coated Substrate
Refers to the coating on what material. The substrate is often determined by the use environment and use. Common coating substrate selection? For example, calcium fluoride substrate is used for gas analysis and protection of gold, float glass for ordinary mirrors, silicon substrate for laser cavity mirrors, silicon germanium for infrared filters, glass for visible and near infrared, nickel and gold for oxygen-free copper.
Calcium fluoride, barium fluoride, magnesium fluoride, sapphire, germanium, silicon, zinc sulfide, zinc selenide, chalcogenide glass, N-BK7, fused silica, etc.
Coating material
Attached to the substrate to play the role of transmission, reflection, light and other materials, may be optical materials such as zinc sulfide, magnesium fluoride, etc., may also be metal, such as aluminum gold. At present, mature large quantities of optical coating materials are mostly granular or flaky, and there are also whole crystal coating targets. Metal coating materials are mostly wire and block. The substrate, purpose and coating index determine what coating material to use.
Previous Page
Next Page
Previous Page
Next Page
online message
Related Products





